Countless words have been written in the last year regarding quantum computing, as it became the hottest potato on the stock exchange. But what is quantum computing? The thing is that most people find it hard to comprehend what quantum computing is in the most basic ways. Don’t worry; I’m here to help you understand the fundamentals of quantum computing, so you won’t feel so lost the next time you read about Google’s (GOOGL) or IonQ’s (IONQ) new advancements. Let’s go!
Confident Investing Starts Here:
- Quickly and easily unpack a company's performance with TipRanks' new KPI Data for smart investment decisions
- Receive undervalued, market resilient stocks straight to you inbox with TipRanks' Smart Value Newsletter
Imagine flipping a coin. In classical physics, the coin is either heads or tails. But in quantum physics, the coin can be both heads and tails at the same time – until you look at it. This strange and counterintuitive nature of the quantum world is at the heart of quantum computing, a technology that challenges everything we know about computing today.
What Is Quantum?
The word “quantum” refers to the smallest possible unit of any physical property. Quantum physics studies the bizarre behavior of subatomic particles, like electrons and photons, that do not follow the classical rules of physics. These particles can exist in multiple states at once, interact with each other instantly across distances, and behave unpredictably until observed.
Quantum Computers vs. Classical Computers
Classical computers, the ones we use today, rely on bits – tiny switches that can be either 0 or 1. These bits work together using transistors to process information in a straightforward, step-by-step manner.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, aim to harness nature’s fundamental rules and power by using qubits instead of bits. Qubits can exist as 0, 1, or both at the same time (thanks to a principle called superposition, which will be explained shortly). This allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of information simultaneously, making them exponentially more powerful for certain types of calculations.
Superposition and Entanglement
Superposition: Imagine a spinning coin again, but instead of just heads or tails, it exists in both states simultaneously until you stop it. This is superposition; qubits can perform multiple calculations simultaneously, giving quantum computers incredible processing power.
Entanglement: Now imagine two magical dice that, no matter how far apart they are, always roll the same number at the same time. This phenomenon is called entanglement, when two qubits become linked so that their states depend on each other, even across vast distances. Entanglement allows quantum computers to share and process information in ways that classical computers cannot.
The Main Players
So now that the basic understanding is there, let’s see what the leading companies are working on:
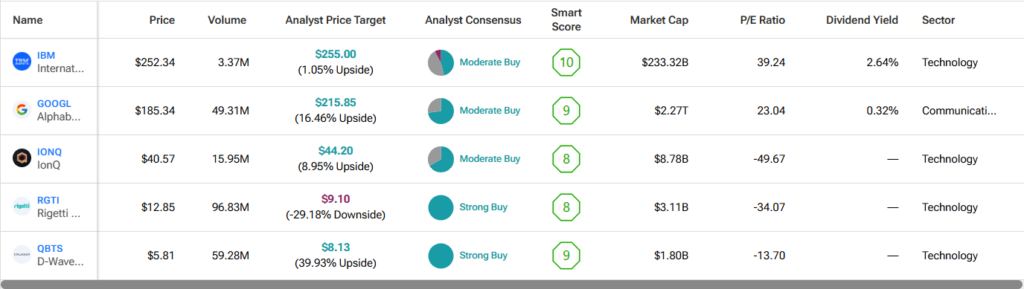
- Google: Google’s Willow quantum processor represents the next step in quantum computing, aiming to build on Sycamore’s achievements with enhanced scalability and error correction techniques.
- IBM: IBM (IBM) Quantum offers cloud-based access to quantum computers, allowing researchers and businesses to experiment with quantum algorithms.
- Rigetti Computing: Rigetti (RGTI) focuses on building superconducting quantum processors and developing hybrid quantum-classical computing solutions.
- IonQ: Unlike Google and IBM, which use superconducting qubits, IonQ utilizes trapped ion technology, where individual atoms serve as qubits and, through laser beams, trap the particles in order to manipulate them for the computing process. This technique offers longer stability.
- D-Wave: D-Wave (QBTS) takes a different approach with quantum annealing, tailored for optimization problems rather than general-purpose quantum computing.
Are You Ready for it?
Quantum computing is still in its early days, but its potential is staggering. As researchers continue to unlock the secrets of the quantum world, we move closer to a future where quantum computers can tackle problems beyond the reach of even the most influential classical supercomputers. The quantum revolution is just beginning—are you ready for it?










